Hi!
Welcome to AIMedily.
Today, Google in partnership with Included Health, announced the launch of a nationwide randomized trial to evaluate conversational AI within real-world virtual care workflows.
This research builds on earlier work about how AI can support clinical reasoning, offer more personalized health insights, and help clinicians navigate complex medical information.
It’s interesting to see big tech companies becoming more involved in healthcare research.
Let’s dive in.
🤖 AIBytes
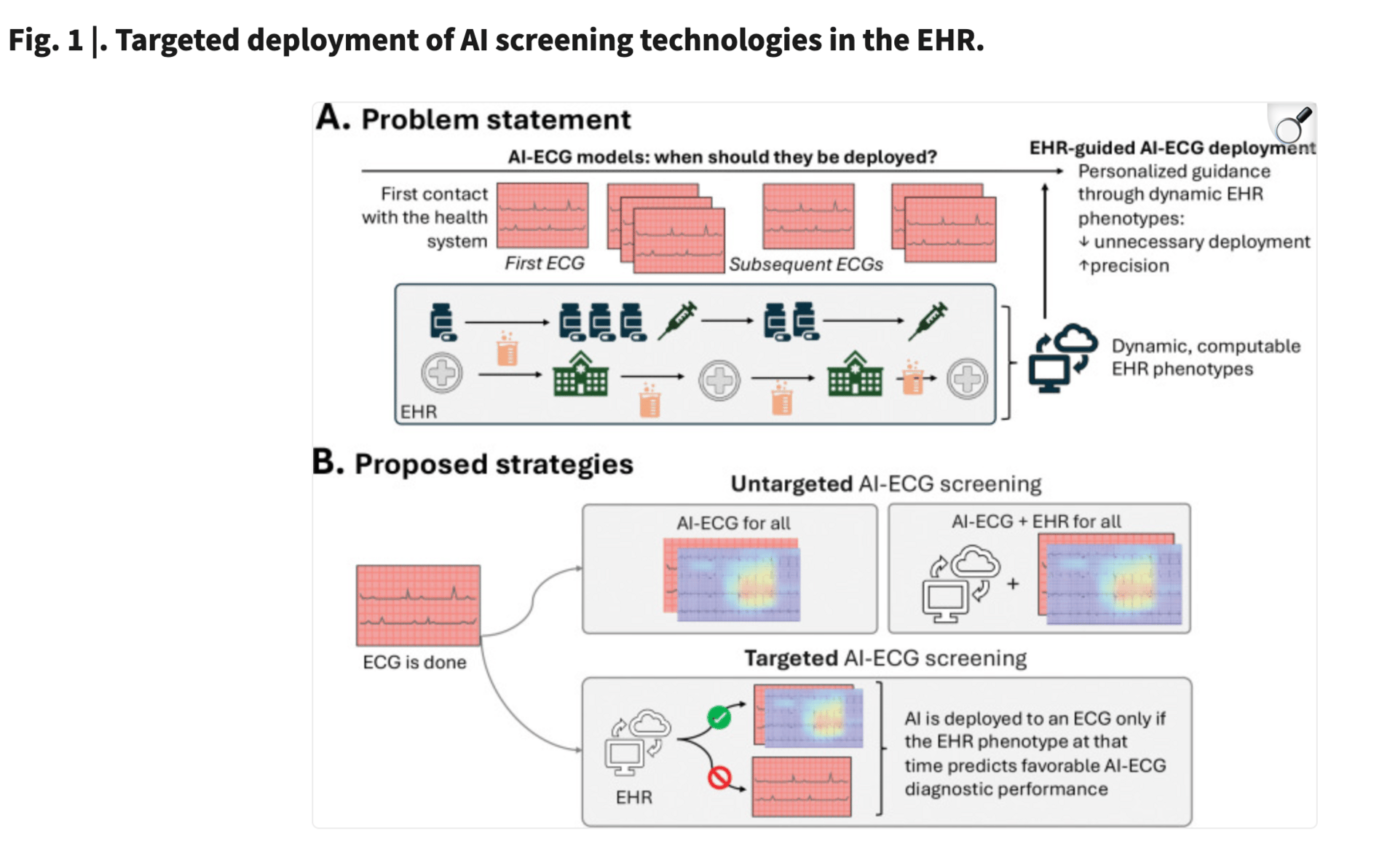
Researchers developed TARGET-AI, a system that combines ECG images with electronic health record data to guide who should be screened for structural heart disease.
🔬 Methods
Patients included:
159,322 adults from a U.S. health system with paired ECG and echocardiogram data
5,198 patients in a temporal validation cohort
33,518 participants from the UK Biobank
3,628 patients from MIMIC-IV
The model aimed to detect 26 types of structural heart disease.
Performance was measured using accuracy and false-positive counts.
📊 Results
The AI-ECG system identified multiple heart conditions, including:
Reduced left ventricular function
Severe aortic stenosis
Elevated right-sided heart pressures
When screening was targeted instead of applied to everyone:
False positives dropped by a median of 303 cases in the temporal validation group
Overall accuracy improved
Sensitivity was largely preserved
Similar reductions in false positives were seen in:
UK Biobank (median reduction 819 cases)
MIMIC-IV (median reduction 255 cases)
🔑 Key Takeaways
Targeted AI-ECG screening improves precision.
False positives are substantially reduced compared with broad screening.
Deployment strategy matters as much as model performance.
Prospective studies in real clinical workflows are still needed.
🔗 Oikonomou EK, Batinica B, Dhingra LS, et al. TARGET-AI: A Foundational Approach for the Targeted Deployment of Artificial Intelligence Electrocardiography in the Electronic Health Record. NEJM AI. 2026;3(2). doi:10.1056/AIoa2500588
The MASAI trial examined whether adding AI to mammography screening changes the risk of cancers missed between screenings, compared with standard double reading by radiologists.
🔬 Methods
Participants: Over 105,000 women.
Groups: AI-supported screening vs standard double reading.
In the AI group, the system supported cancer detection and helped decide when single or double reading was needed.
Primary outcome: Interval cancer rate.
Secondary outcomes: Sensitivity, specificity, and tumor characteristics.
📊 Results
Interval cancer rates were similar between groups and met criteria for non-inferiority.
Sensitivity was higher with AI-supported screening.
Specificity remained unchanged.
Interval cancers after AI-supported screening tended to have less aggressive features, including fewer large and invasive tumors.
Earlier MASAI analyses showed a substantial reduction in radiologist workload, without more false positives.
🔑 Key Takeaways
AI-supported mammography did not increase interval cancer risk.
Cancer detection improved without sacrificing specificity.
Interval cancers that did occur appeared less aggressive.
AI may help strengthen screening programs, especially where radiologist capacity is limited.
Longer follow-up and cost-effectiveness data are still needed.
🔗 Gommers J, Hernström V, Josefsson V, et al. AI-supported mammography screening vs standard double reading in the MASAI study: a randomized noninferiority trial. Lancet. 2026;407(10527):505-514. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)02464-X.
🦾TechTools
Conversational mental health support based on evidence-based approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy.
Designed to help patients manage mood, stress, and anxiety between or outside clinical visits.
The tool is used mainly in research and population health settings, with clear limits around diagnosis and clinical oversight.
HIPAA-compliant electronic health record (EHR) designed for independent and primary care practices.
It focuses on simplifying clinical workflows, documentation, and patient management rather than adding complex enterprise features.
Most commonly used in outpatient settings.
Cloud-based work management platform for planning, tracking, and automating work.
Used by organizations to coordinate projects, processes, and collaboration at scale.
Supports workflows, reporting, and integrations to reduce manual work.
🧬AIMedily Snaps
What to expect in US healthcare in 2026 and beyond (Link).
AI can predict preemies’ path, Stanford Medicine-led study shows (Link).
What are the best AI tools for research? Nature’s guide (Link).
Google AI Overviews cite YouTube more than any medical site for health queries, study suggests (LInk).
AI Tool Helps Predict Which Patients Need Continued Care After Leaving the Hospital (Link).
Boston Children’s finds patient ‘doppelgangers’ 5x faster with AI (Link).
🧪 Research Signals
Designing Clinically Useful AI: A Blueprint for Impact (Link).
The Missing Dimension in Clinical AI: Making Hidden Values Visible (Link).
Invisible Text Injection and Peer Review by AI Models (Link)
Augmenting Surgical Preparation: How Learners Use Artificial Intelligence to Prepare for the Operating Room (Link).
Ambient Artificial Intelligence Scribes and Physician Financial Productivity (Link).
Ambient AI Tool Adoption in US Hospitals and Associated Factors (Link).
🧩TriviaRX
Which technology was first introduced in hospitals in the 1960s and quietly transformed patient safety by continuously tracking vital signs?
A) Pulse oximetry
B) Bedside cardiac monitoring
C) Automated blood pressure cuffs
D) Smart infusion pumps
Here is the answer from last week TriviaRX:
✅ B) CPOE systems were among the first digital health tools shown to significantly reduce medication errors in hospitals by eliminating handwritten orders and integrating basic safety checks.
That’s it for today.
I appreciate you time.
If you enjoyed this read, the best compliment I could receive would be if you shared it.
Forward AIMedily to your colleagues who’d appreciate the insights.
Until next Wednesday.
Itzel Fer, MD PM&R
Forwarded this email? Sign up here
P.S. Enjoying AIMedily? 👉 Write a review here (it takes less than a minute).





